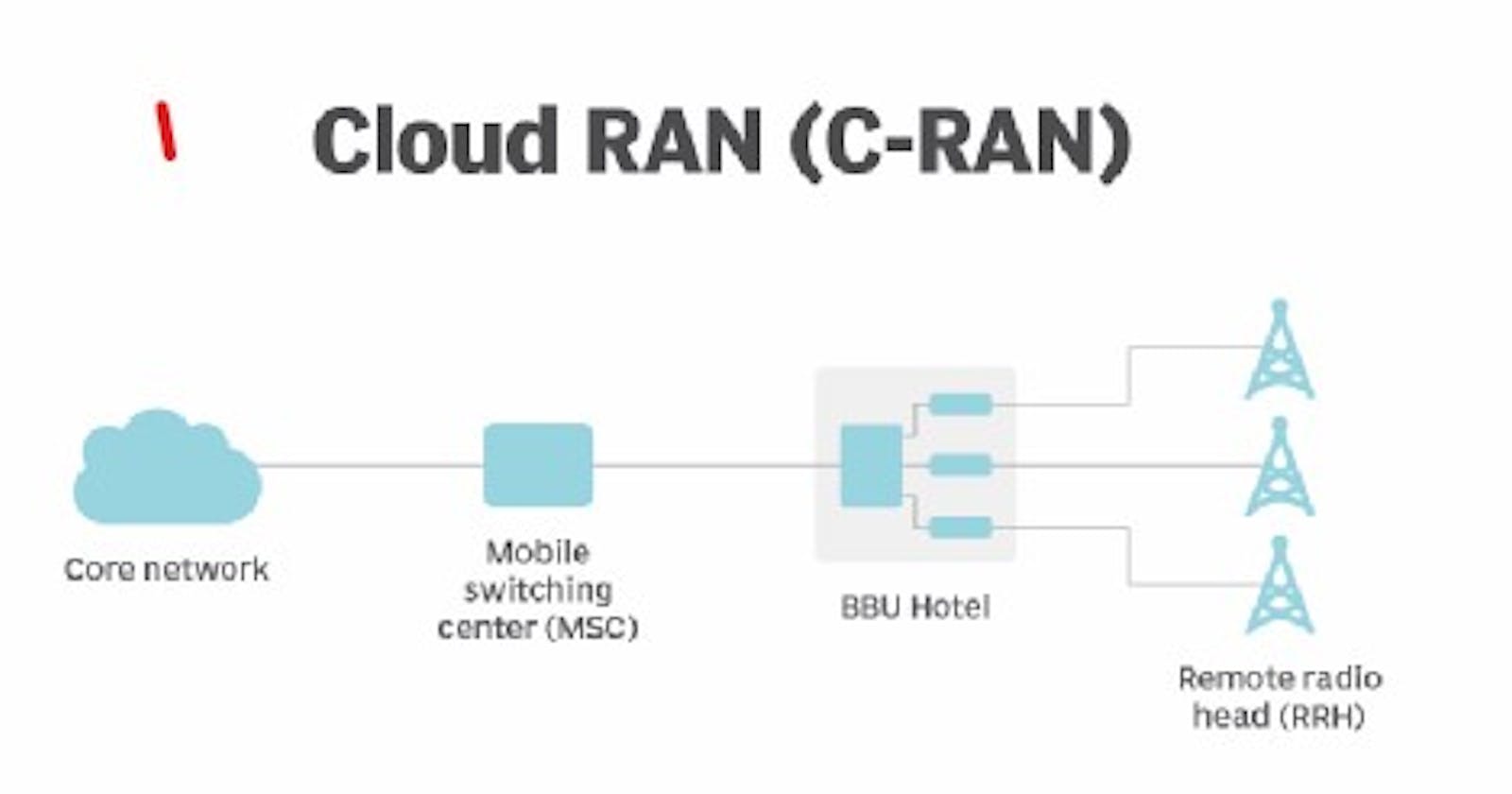
Introduction:
The world of telecommunications is undergoing a major transformation, driven by the rapid advancement of cloud computing technologies. One of the most significant developments in this field is the emergence of Cloud-Enabled Radio Access Network (RAN). This innovative approach is set to revolutionize the way wireless networks are designed, deployed, and managed, promising unprecedented levels of scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of Cloud-Enabled RAN and its potential to shape the future of wireless communication.
Understanding Cloud-Enabled RAN:
Radio Access Network (RAN) forms a crucial component of wireless networks, responsible for connecting user devices to the core network infrastructure. Traditionally, RAN has been implemented as a distributed and hardware-intensive architecture, with base stations and other network elements deployed at various locations. However, Cloud-Enabled RAN introduces a paradigm shift by centralizing and virtualizing the RAN functions.
Cloud-Enabled RAN leverages the power of cloud computing to consolidate and virtualize RAN functions, allowing them to be executed on standard servers located in centralized data centers. This consolidation brings several benefits, including enhanced resource utilization, dynamic allocation of network resources, and centralized management and orchestration of the RAN. It enables network operators to scale their networks efficiently, optimize capacity allocation, and introduce new services with greater agility.
Key Advantages of Cloud-Enabled RAN:
Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud-Enabled RAN enables network operators to scale their networks in a more flexible and cost-effective manner. By leveraging the cloud's virtualization capabilities, operators can dynamically allocate resources based on network demand, ensuring optimal utilization of infrastructure. This scalability allows networks to handle the ever-increasing data traffic, especially in densely populated areas and during peak usage periods.
Cost Efficiency: With Cloud-Enabled RAN, network operators can significantly reduce their capital and operational expenditures. By centralizing RAN functions, operators can avoid the need for deploying and maintaining numerous base stations at various locations. This consolidation leads to cost savings in terms of infrastructure, power consumption, and maintenance. Additionally, the use of commodity hardware and virtualized software reduces the need for specialized proprietary equipment, further driving down costs.
Network Optimization: Cloud-Enabled RAN enables intelligent network optimization through advanced analytics and real-time monitoring. By collecting and analyzing vast amounts of data from the network, operators can gain insights into user behavior, traffic patterns, and network performance. This information can be utilized to optimize resource allocation, improve coverage, and enhance overall network efficiency, resulting in an improved user experience.
Service Agility: The virtualized nature of Cloud-Enabled RAN allows for rapid service deployment and innovation. Operators can introduce new services and features more quickly, leveraging the flexibility and programmability of virtualized network functions. This agility enables operators to adapt to changing market demands, launch new services rapidly, and provide a competitive edge in the telecommunications industry.
Challenges and Considerations:
While Cloud-Enabled RAN brings numerous advantages, there are also some challenges and considerations that need to be addressed:
Latency: The centralized nature of Cloud-Enabled RAN introduces additional latency compared to traditional distributed RAN architectures. This latency can impact real-time applications and services that require ultra-low latency, such as autonomous vehicles or remote robotic surgery. To mitigate this challenge, edge computing and network slicing techniques can be employed to reduce latency and ensure optimal service delivery.
Network Security: Centralization and virtualization of RAN functions raise concerns regarding network security and privacy. Operators need to implement robust security measures to protect the virtualized network functions, data transmission, and user privacy. Encryption, access control mechanisms, and threat detection systems must be implemented to mitigate potential security risks.
Infrastructure Requirements: Cloud-Enabled RAN requires a robust and reliable cloud infrastructure to support the virtualized RAN functions. Data centers with high computing power, low-latency network connectivity, and efficient storage capabilities are essential for ensuring the success of Cloud-Enabled RAN deployments.
Conclusion:
Cloud-Enabled RAN represents a significant advancement in wireless network architecture, offering network operators enhanced scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. By centralizing and virtualizing RAN functions, operators can optimize resource allocation, deploy services more rapidly, and adapt to evolving market demands. However, challenges related to latency, security, and infrastructure must be carefully addressed to unlock the full potential of Cloud-Enabled RAN. As cloud computing technologies continue to evolve, we can expect to see Cloud-Enabled RAN playing a pivotal role in shaping the future of wireless communication, enabling the seamless connectivity required for the emerging technologies and applications of tomorrow.